The greenhouse effect is the way in which heat is trapped close to Earth's surface by "greenhouse gases" These heattrapping gases can be thought of as a blanket wrapped around Earth, keeping the planet toastier than it would be without them Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxidesGREAT LAKES CLIMATE CHANGE CURRICULUM GREENHOUSE GASES BACKGROUND The Earth's climate depends on the amount of solar radiation received and the atmospheric abundance of clouds and greenhouse gases The main greenhouse gases are carbon dioxide, methane, chlorofluorocarbons, nitrous oxide, water vapor, and ozone Much of the highenergy,Climate change includes both humaninduced global warming and its largescale impacts on weather patterns There have been previous periods of climate change, but the current changes are more rapid than any known events in Earth's history The main cause is the emission of greenhouse gases, mostly carbon dioxide (CO 2) and methaneBurning fossil fuels for energy

Climate Change Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Noaa Climate Gov
Climate change greenhouse gases graph
Climate change greenhouse gases graph- Playing it conservative with the EU figures and extrapolating from the scarce figures that exist for other countries, we can estimate that at least 56% of emissions are due to food transport, 810% due to food processing and packaging, around 12% due to refrigeration, and 12% due to retailClimate change widespread, rapid, and intensifying – IPCC — GENEVA, Aug 9 – Scientists are observing changes in the Earth's climate in every region and across the whole climate system, according to the latest Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) Report, released today
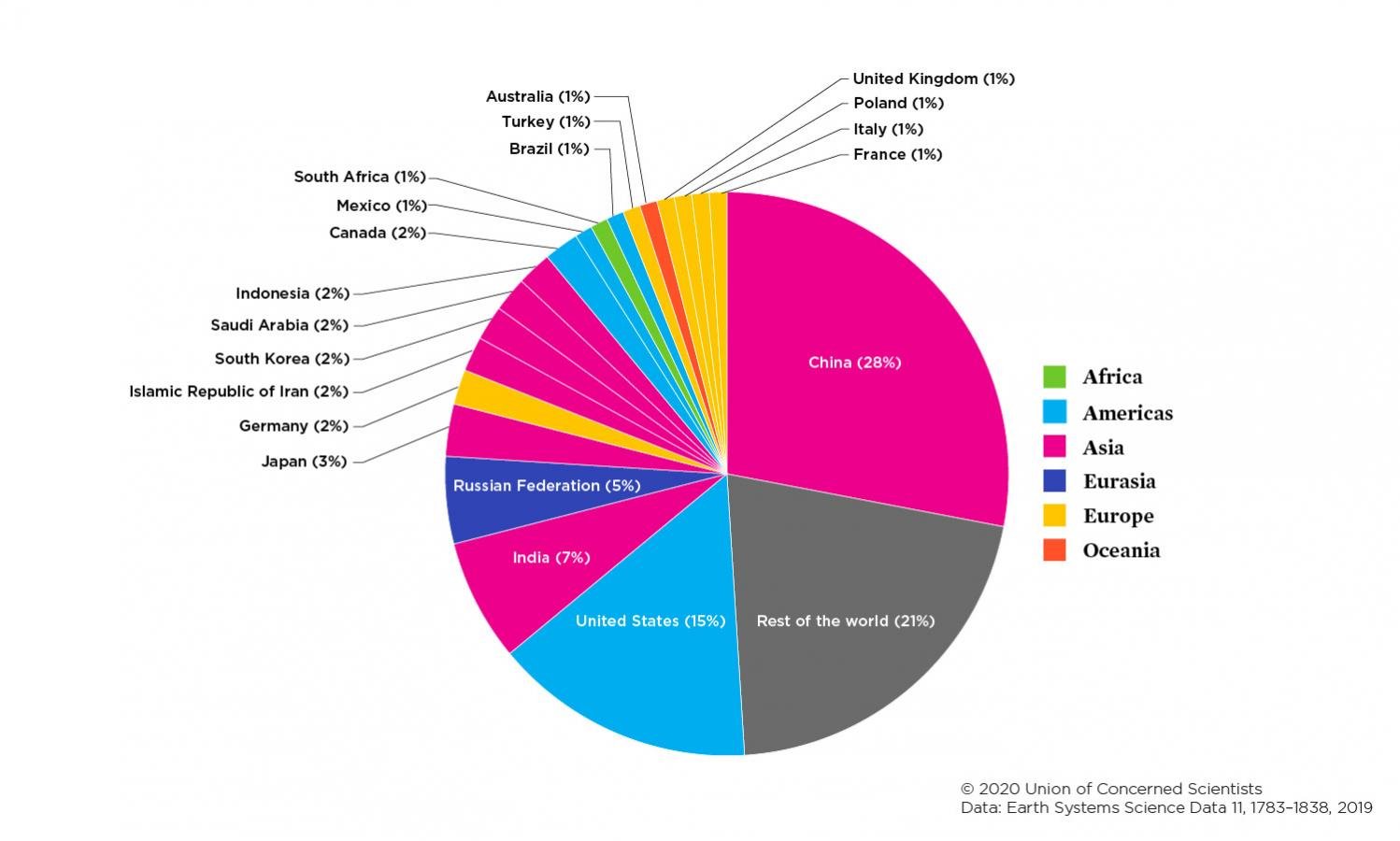



Each Country S Share Of Co2 Emissions Union Of Concerned Scientists
Greenhouse gas emissions Greenhouse gas emissions Climate change is one of the most important environmental issues of our time Note The chart presents the ratio of annual greenhouse gas emissions per person and per unit of gross domestic product relative to thoseLonglived gases that remain semipermanently in the atmosphere and do not respond physically or chemically to changes in temperature are described as "forcing" climate change Gases, such as water vapor, which respond physically or chemically to changes in temperature are seen as "feedbacks" Gases that contribute to the greenhouse effect include Carbon dioxide (CO 2) is an important heattrapping (greenhouse) gas, which is released through human activities such as deforestation and burning fossil fuels, as well as natural processes such as respiration and volcanic eruptions The first graph shows atmospheric CO 2 levels measured at Mauna Loa Observatory, Hawaii, in recent years, with
Greenhouse gases emitted by human activities alter Earth's energy balance and thus its climate Humans also affect climate by changing the nature of the land surfaces (for example by clearing forests for farming) and through the emission of pollutants that affect the amount and type of particles in the atmosphereAgriculture's greenhouse gas emissions cows and grazing land In Australia, 'agriculture' contributes around 13% of our greenhouse gas emissions each year By weight, about half of the agricultural sector's emissions – or 42% – are methane Most of this is the methane produced by cows and other livestock due to the fermentation ofTo prevent severe climate change we need to rapidly reduce global greenhouse gas emissions The world emits around 50 billion tonnes of greenhouse gases each year measured in carbon dioxide equivalents (CO 2 eq) 1 To figure out how we can most effectively reduce emissions and what emissions can and can't be eliminated with current technologies, we need to first
US Greenhouse Gas Emissions by Gas, 1990–19 This figure shows emissions of carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and several fluorinated gases in the United States from 1990 to 19 For consistency, emissions are expressed in million metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalents * HFCs are hydrofluorocarbons, PFCs are perfluorocarbons, SF6 is Greenhouse gas emissions by sector in the EU According to the fifth assessment report by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), it is extremely likely that human activities over the past 50 years have warmed our planet These activities include for example the burning of coal, oil and gas, deforestation and farming General The Interactive Data Visualization tool gives users a way to explore the abundance of different gases at more than 0 sampling sites around the world You can view graphs showing how the amount of carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, ozone, and various chlorofluorocarbons have changed over time at any NOAA sampling site




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Are Set To Rise Fast In 21 The Economist
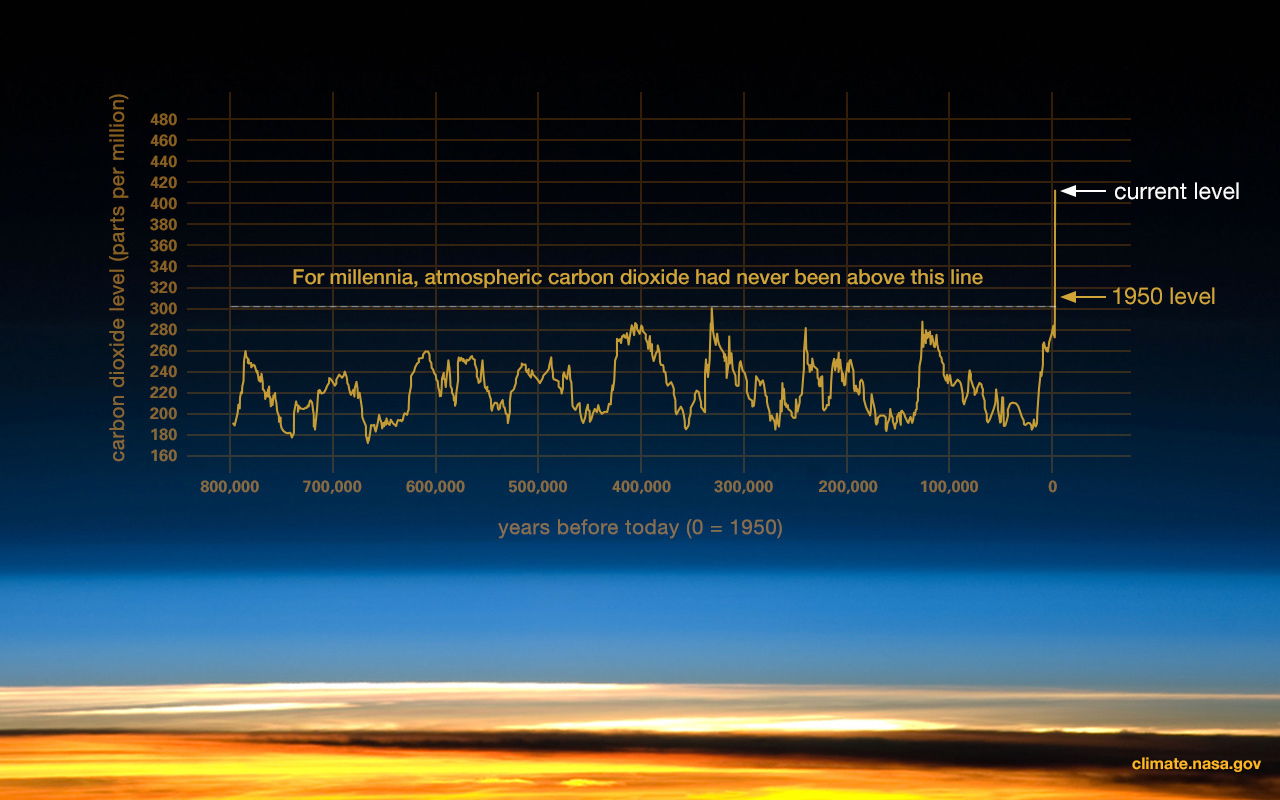



Evidence Facts Climate Change Vital Signs Of The Planet
Climate Change Indicators Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions This indicator describes emissions of greenhouse gases worldwide Figure 1 Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions by Gas, 1990–15 This figure shows worldwide emissions of carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and several fluorinated gases from 1990 to 15Where does it come from?This chart maps out future greenhouse gas emissions scenarios under a range of assumptions if no climate policies were implemented;
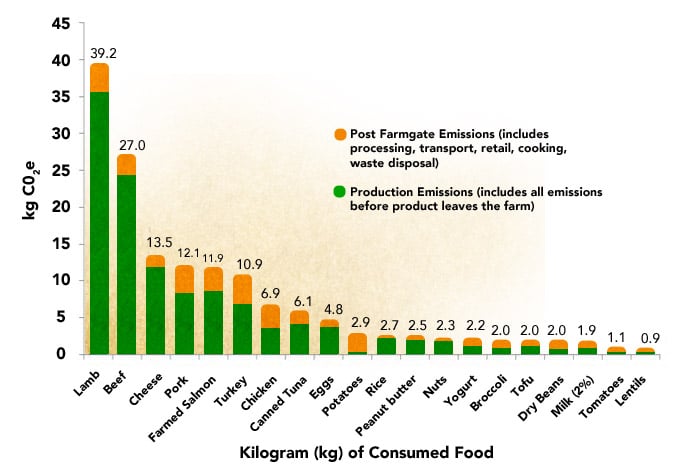



The Impacts 11 Meat Eaters Guide Meat Eater S Guide To Climate Change Health Environmental Working Group
.png)



Greenhouse Gas Emissions From Waste Products Eurostat News Eurostat
This indicator describes how the levels of major greenhouse gases in the atmosphere have changed over time Figure 1 Global Atmospheric Concentrations of Carbon Dioxide Over Time This figure shows concentrations of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere from hundreds of thousands of years ago through 19, measured in parts per million (ppm)If current policies continued;Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas Too much of it in the air is dangerous for the Earth The information in this graph is evidence for climate




This Graph Shows How The Total Amount Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Has Been Increasing Around The World Greenhouse Gases Climate Change Greenhouse Gas Emissions
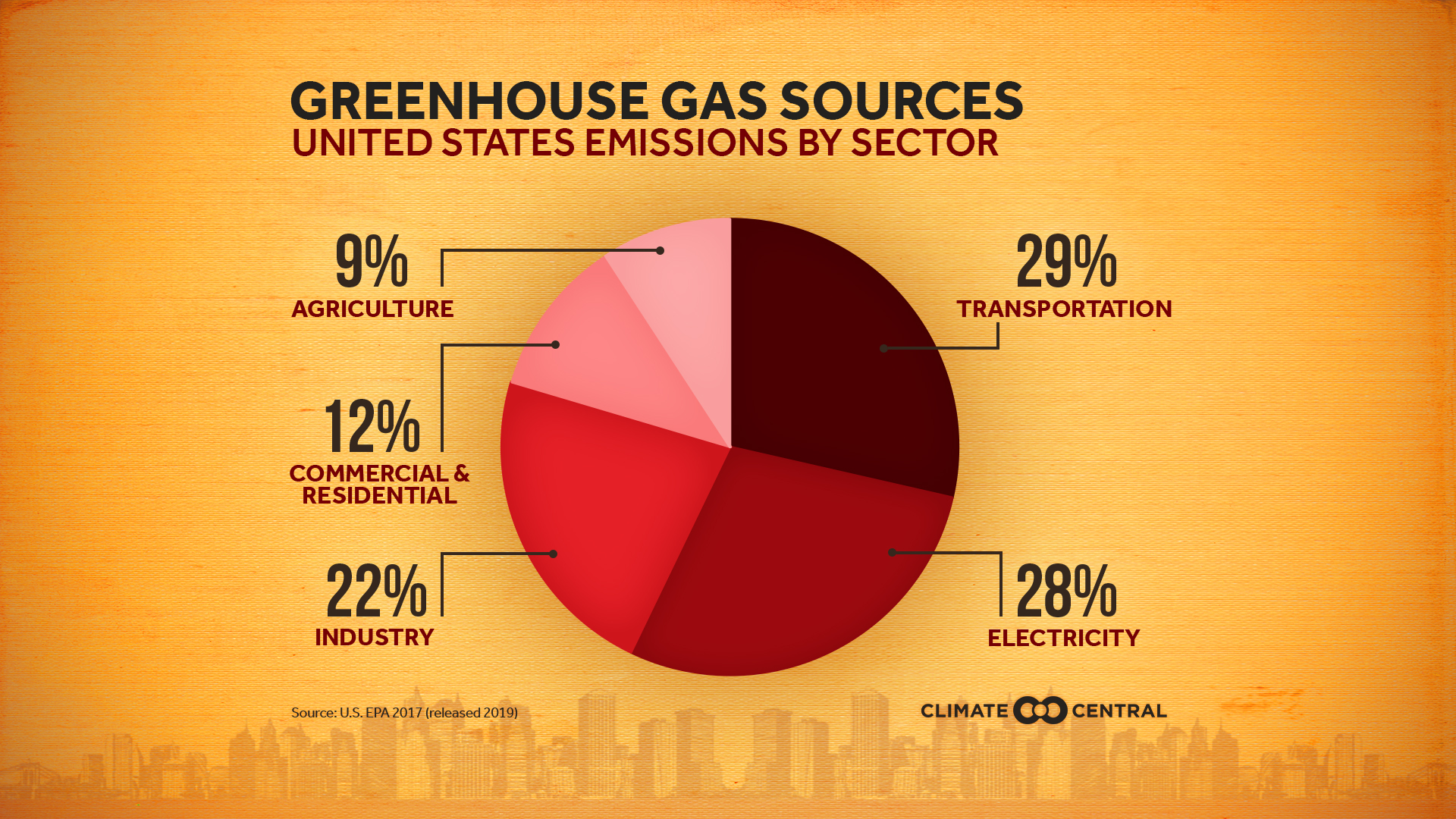



Emissions Sources Climate Central
Main Greenhouse Gases Multiple gases contribute to the greenhouse effect that sets Earth's temperature over geologic time Small changes in the atmospheric concentration of these gases can lead to changes in temperature that make the difference between ice ages when mastodons roamed the Earth, and the sweltering heat in which the dinosaurs livedAnd necessary pathways which are compatible with limiting warming to 15°C or 2°C of warming this century 14Earths Greenhouse Gases LT 21 Green House Gases I can explain what causes greenhouse gases (natural and unnatural) and how the role these gases play in the atmosphere Greenhouse gases Concentration (how much) Ability to trap heat (GWP) Bigger numbers means more warming How long does it stay in air?
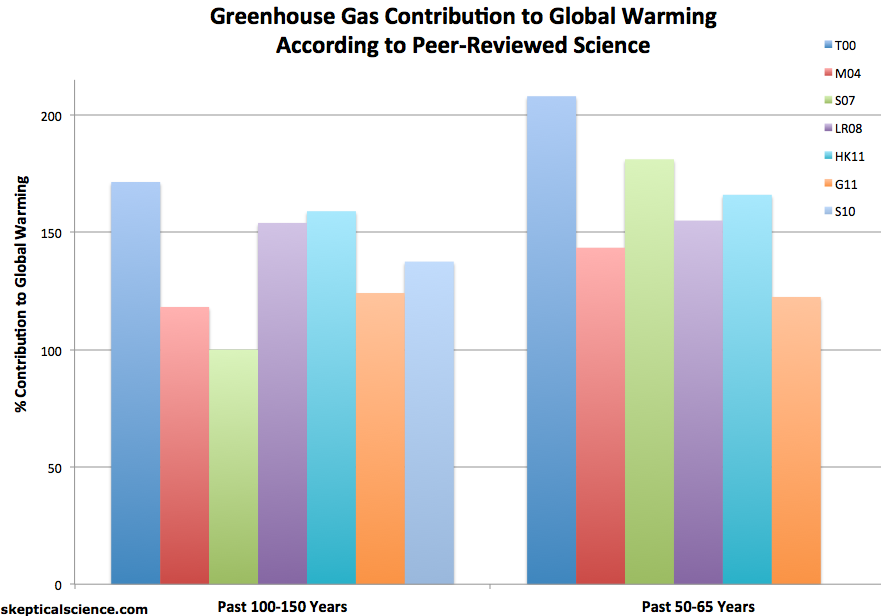



How Do We Know More Co2 Is Causing Warming




Germany S Greenhouse Gas Emissions And Energy Transition Targets Clean Energy Wire
At its 47th Session on 1316 March 18, the IPCC adopted Decision IPCCXLVII9 where TGICA was renamed to Task Group on Data Support for Climate Change Assessments (TGData) with new Terms of Reference for TGData as well as Guidance for the Data Distribution Centre (DDC) Membership TGData members were selected during the 56th Session ofGreenhouse gases (ghg), although they constitute only a small fraction of the atmosphere, their impact on climate is very important Without greenhouse gases, the Earth's surface would have an average temperature of 18oC, too cold for life as we know it Instead the average temperature at the surface of the Earth is approximately 15oCThe graph to the right shows which activities produce the most greenhouse gases in the United States These greenhouse gases don't just stay in one place after they're added to the atmosphere As air moves around the world, greenhouse gases become globally mixed, which means the concentration of a greenhouse gas like carbon dioxide is roughly the same no matter




Climate Change Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Noaa Climate Gov
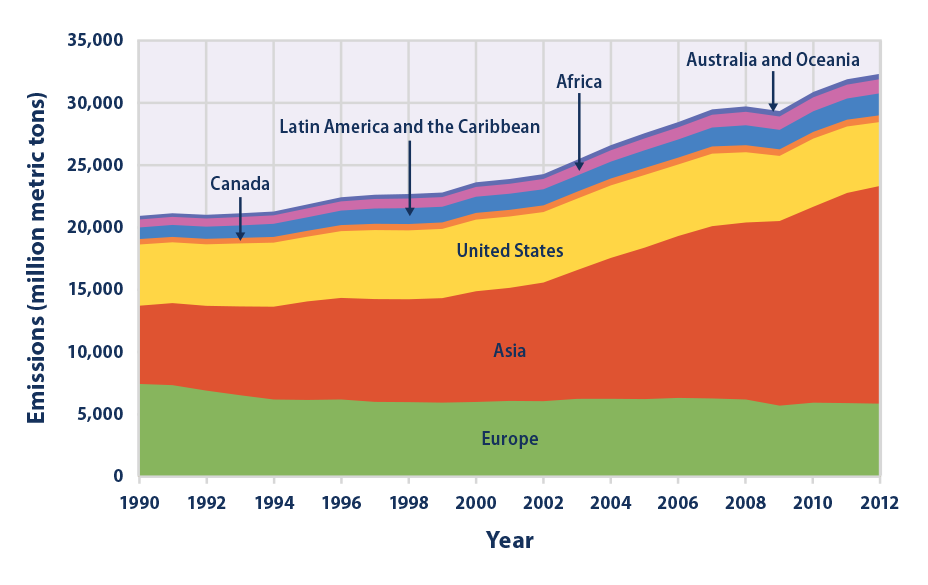



Climate Change Indicators Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Climate Change Indicators In The United States Us Epa
Climate Change Impacts and Agricultural Adaptation Climate change has the potential to adversely impact agricultural productivity at local and regional scales through alterations in rainfall patterns, more frequent occurrences of climate extremes (including high temperatures or drought), altered patterns of pest pressure, and changes in seasonal andThe greenhouse gases in the atmosphere can both absorb and reradiate much of the outgoing heat energy The atmospheric concentrations of some greenhouse gases are being affected directly by human activities namely carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), methane (CH 4 ), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), ozone (O 3 ), and synthetic gases, such as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and hydrofluorocarbons • Climate change causes living graph worksheet Methodology and teacher notes This activity graphically demonstrates to students the extent different causes (or scientifically known as 'forcings') of climate change since we have began keeping temperature observations The way the data has been visualised for this activity has been simplified from extensive research and climate




Climate Change How Quickly Are We Emissions Reducing World Economic Forum
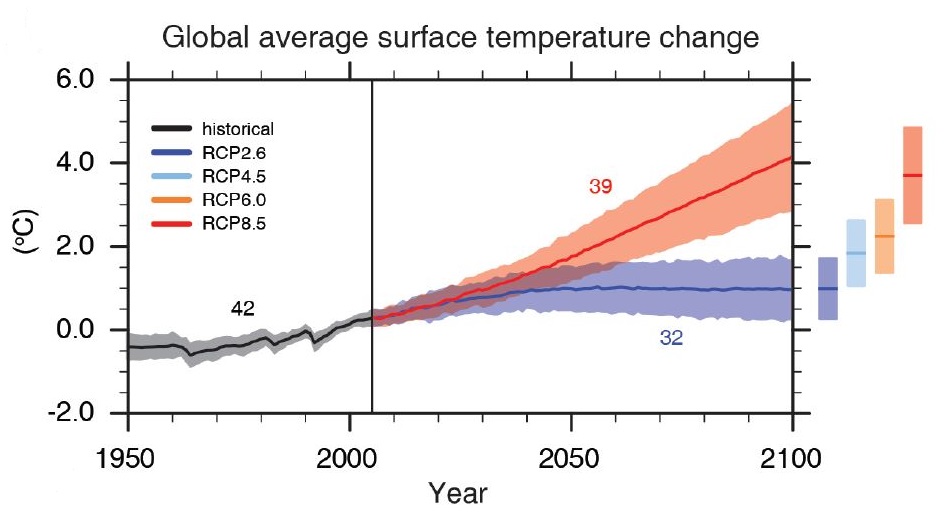



Ipcc Six Graphs That Explain How The Climate Is Changing Carbon Brief
Based on data from the WRI's CAIT Climate Data Explorer, the graphic shows emissions data from 12 by country As a whole, the world emitted 42,386 megatonnes of greenhouse gases Here's how Graph by NOAA Climategov, adapted from Figure 36 in State of the Climate in 19 See original figure for details about data sources and uncertainty Less than a watt per square meter might seem like a small change, but multiplied by the surface area of the ocean (more than 360 million square kilometers), that translates into an enormous global energy imbalance Aviation accounts for around 25% of global CO 2 emissions, but it's overall contribution to climate change is higher This is because air travel does not only emit CO 2 it affects the climate in a number of more complex ways As well as emitting CO 2 from burning fuel, planes affect the concentration of other gases and pollutants in the atmosphere
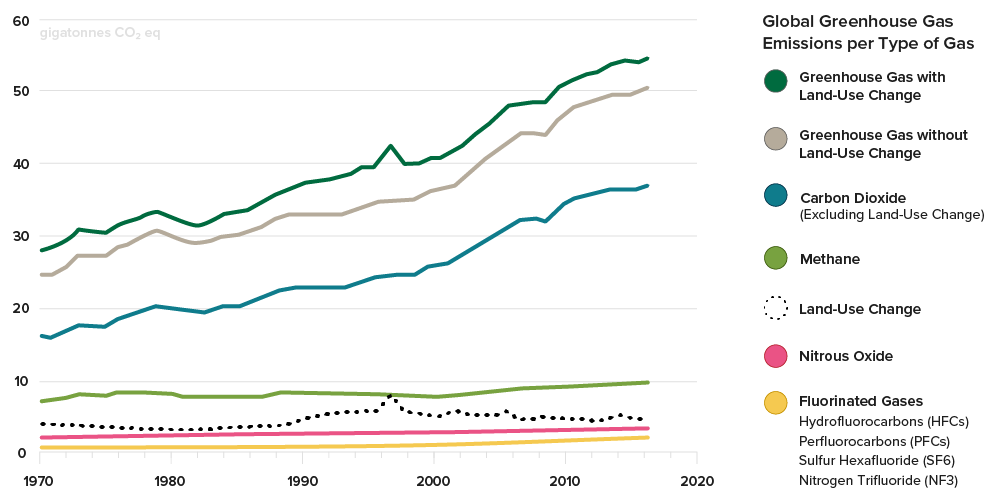



Carbon Emissions Forestry Carbon Credits The Arbor Day Foundation



Chart China Beats U S Europe In Combined Greenhouse Gases Statista
The energy sector is central to efforts to combat climate change Promoting sustainable development and combating climate change have become integral aspects of energy planning, analysis and policy making Energy accounts for twothirds of total greenhouse gas, so efforts to reduce emissions and mitigate climate change must include the energyAn overview of the greenhouse effect and other contributors to abrupt climate change Graphic Global Warming from 10 to 19 A visualization of global temperature changes since 10 based on NASA GISS dataIf all countries achieved their current future pledges for emissions reductions;
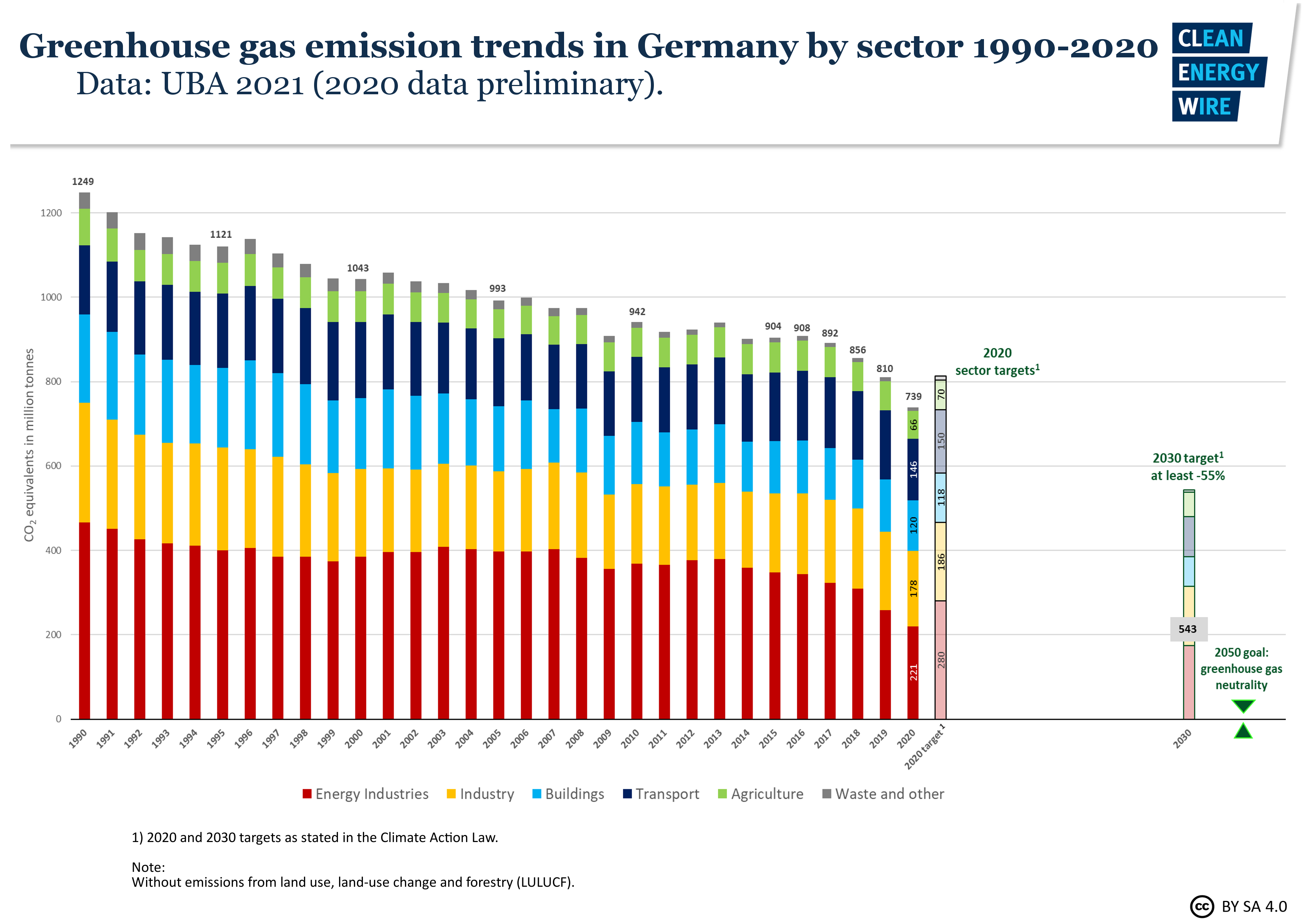



Germany Sees Record Greenhouse Gas Emission Fall Due To Pandemic Renewables Clean Energy Wire




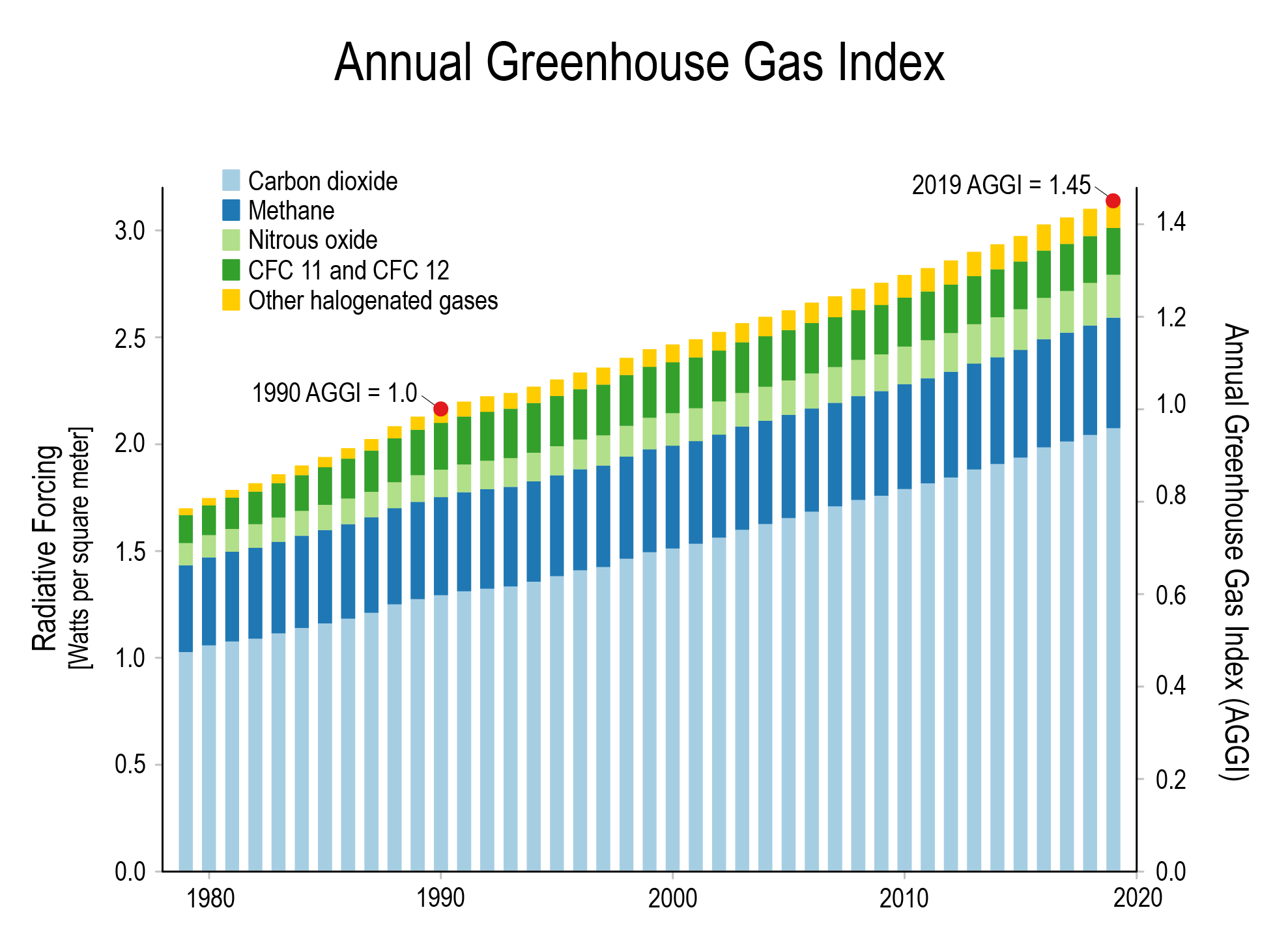
Noaa Global Monitoring Laboratory The Noaa Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Aggi
What does it actually mean? In 19 the UN's Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change estimated that the global food system was responsible for 2137% of GHG emissions The 'greenhouse effect' is the warming of climate that results when the atmosphere traps heat radiating from Earth toward space Certain gases in the atmosphere resemble glass in a greenhouse, allowing sunlight to pass into the 'greenhouse,' but blocking Earth's heat from escaping into space The gases that contribute to the greenhouse effect include water vapor,




Topic 1 Observed Changes And Their Causes Ipcc




Temperature Change And Carbon Dioxide Change National Centers For Environmental Information Ncei Formerly Known As National Climatic Data Center Ncdc
An increase in the atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gases produces a positive climate forcing, or warming effect From 1990 to 19, the total warming effect from greenhouse gases added by humans to the Earth's atmosphere increased by 45 percent The warming effect associated with carbon dioxide alone increased by 36 percentThis chart shows the change in global greenhouse gas emissions over time Greenhouse gases are measured in 'carbon dioxideequivalents' (CO 2 e) Today, we collectively emit around 50 billion tonnes of CO 2 e each year This is more than 40% higher than emissions in 1990, which were around 35 billion tonnes But although most climate targets aim to reduce greenhouse gas emissions as a group, the essential ingredient is carbon dioxide The graph above illustrates why
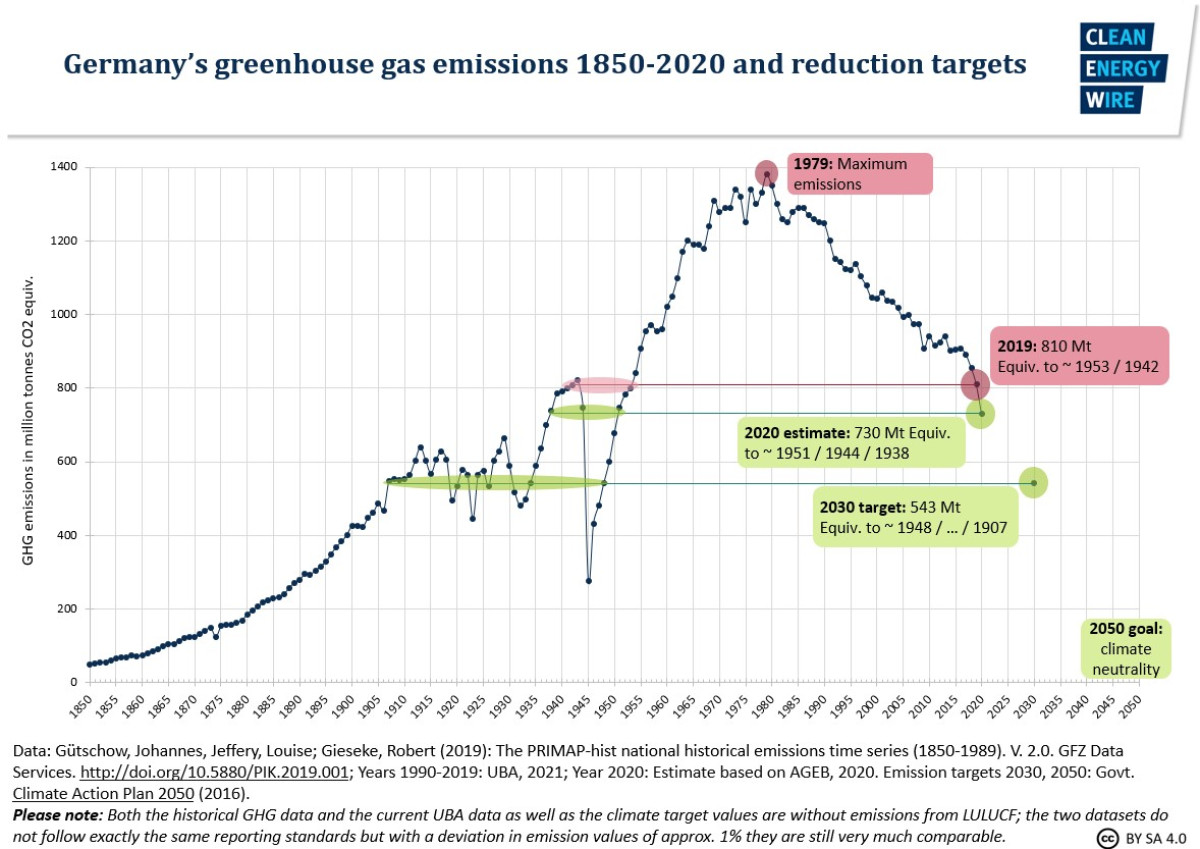



Germany S Greenhouse Gas Emissions And Energy Transition Targets Clean Energy Wire




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa
This graph shows that the amount of carbon dioxide in the air in Hawaii has been slowly and steadily increasing for the last 45 years 4 Think big Why is this important? Much is written about the impact of carbon dioxide (CO 2) on climate change to the extent that the perception can arise that it alone is responsible for climate warmingIn fact the chief greenhouse gas (GHG) is water vapour but as this is relatively fixed and not too obvious a candidate for manipulation it tends to be disregarded




The Business Of Climate Change The Economist




Cause And Effect For Global Warming Time For Change




Global Warming
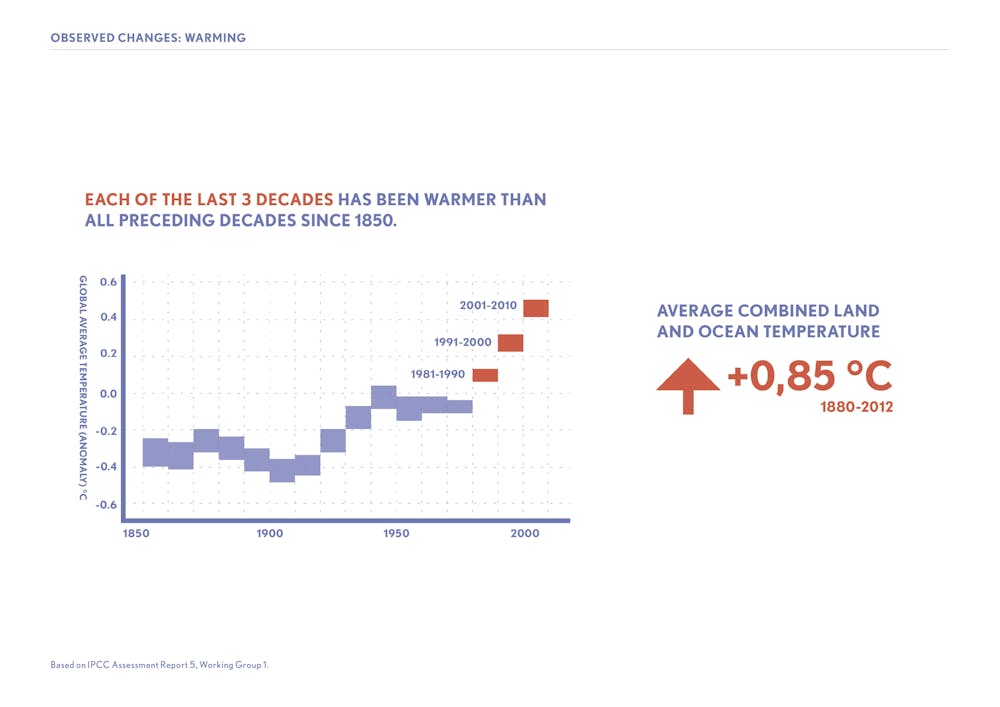



What Would Happen To The Climate If We Stopped Emitting Greenhouse Gases Today
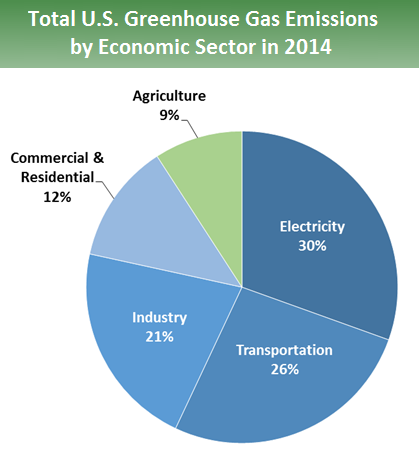



Sources Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Us Epa




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa




The Science Of Carbon Dioxide And Climate
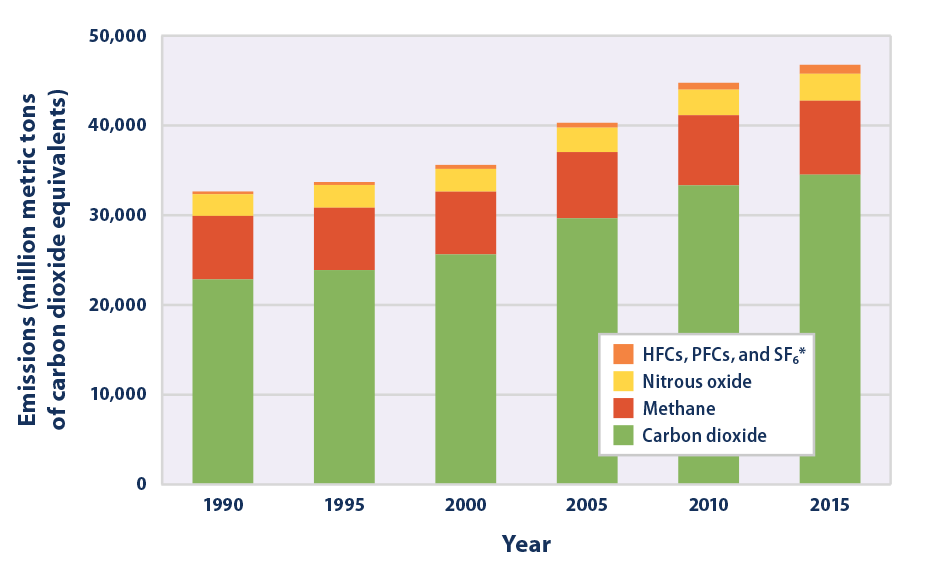



Climate Change Indicators Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Us Epa




Are Humans Causing Or Contributing To Global Warming Noaa Climate Gov
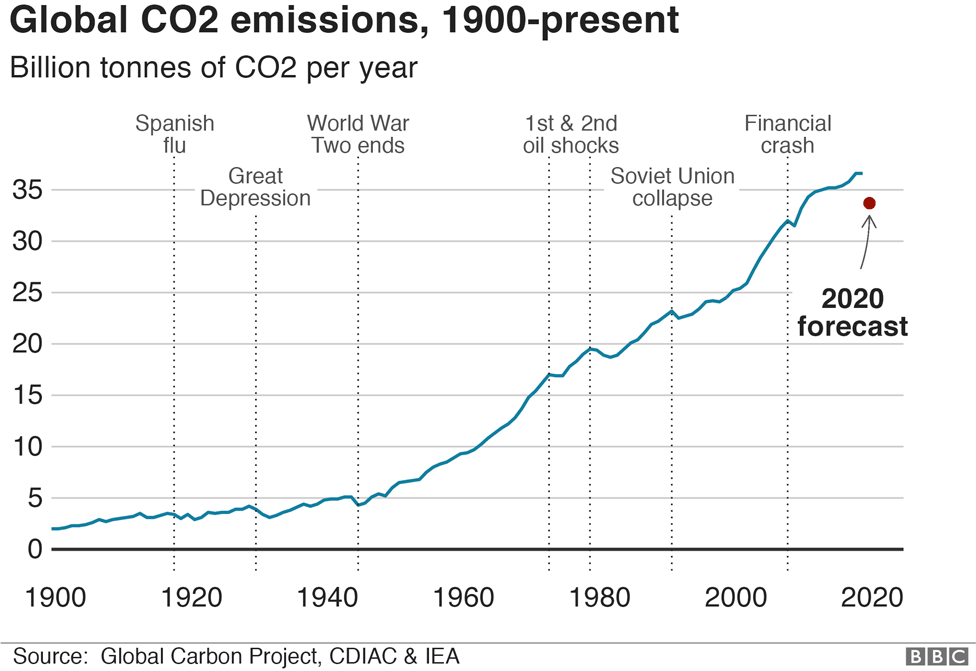



Climate Change And Coronavirus Five Charts About The Biggest Carbon Crash c News
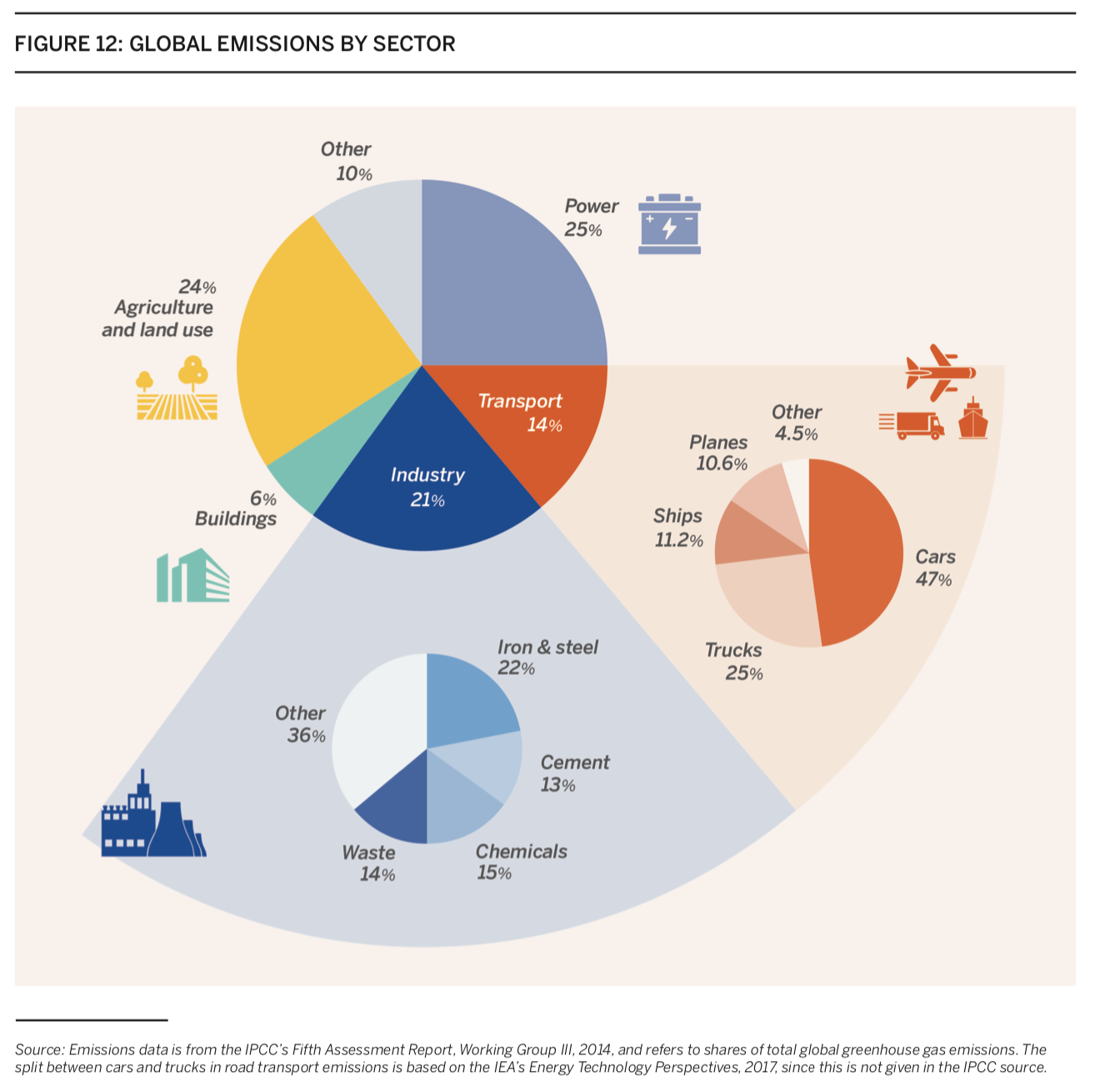



Charts Of The Week Tackling Climate Change




Saskatchewan S New Climate Change Strategy Reckless Endangerment Darrin Qualman



Co And Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data




Which Gases Are Greenhouse Gases American Chemical Society



1
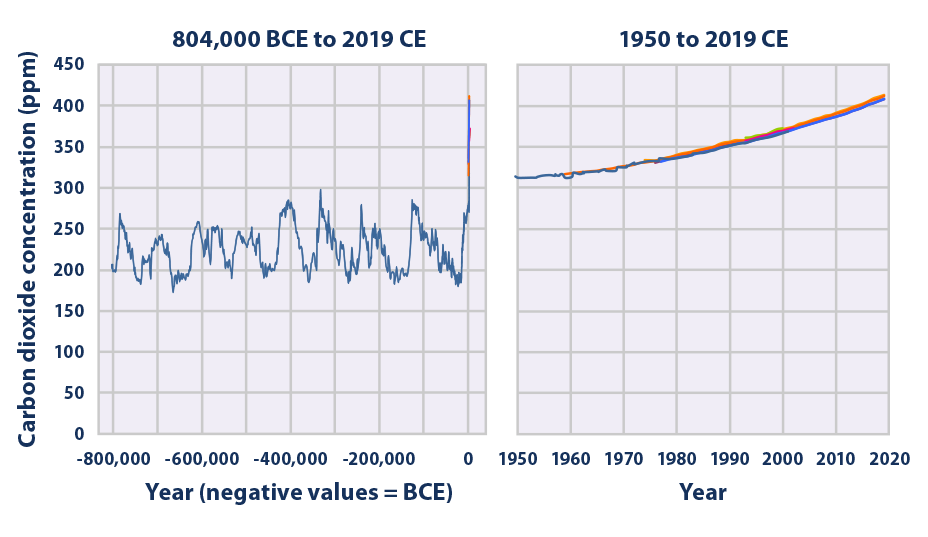



Climate Change Indicators Atmospheric Concentrations Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Greenhouse Gases Have Soared To Record Levels Wmo Climate Central



The Three Most Important Graphs In Climate Change Climate And Agriculture In The Southeast



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Greendallas
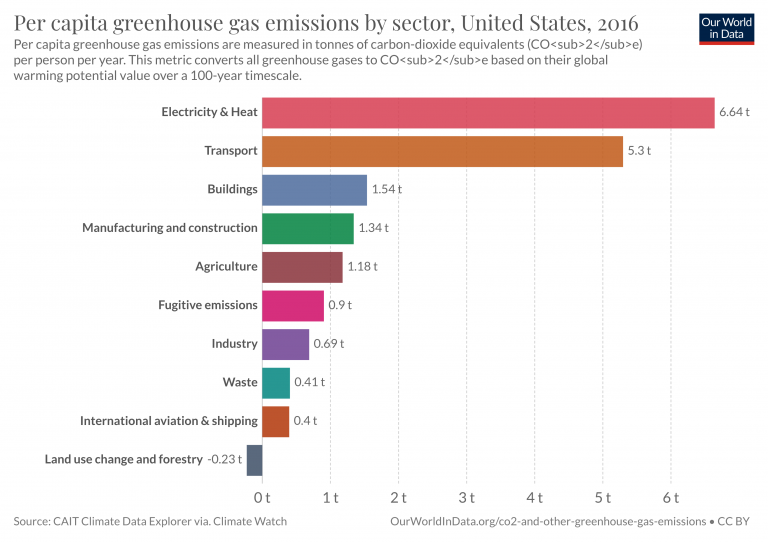



Emissions By Sector Our World In Data



Greenhouse Gas Global Greenhouse Warming
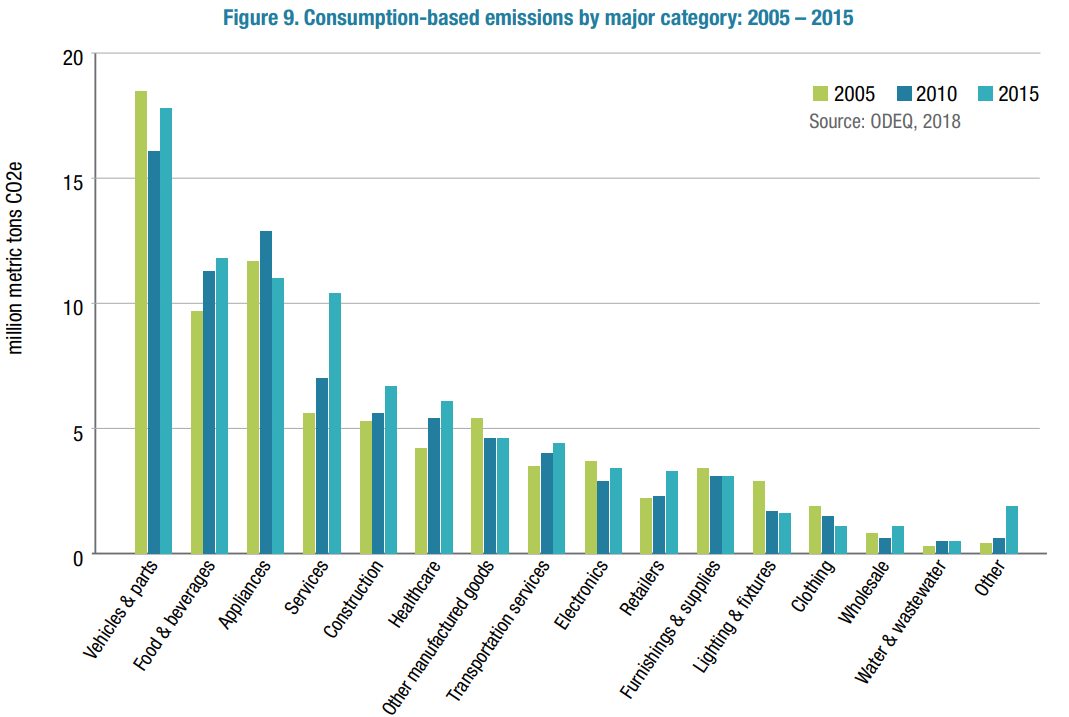



State Of Oregon Energy In Oregon Greenhouse Gas Emissions Data
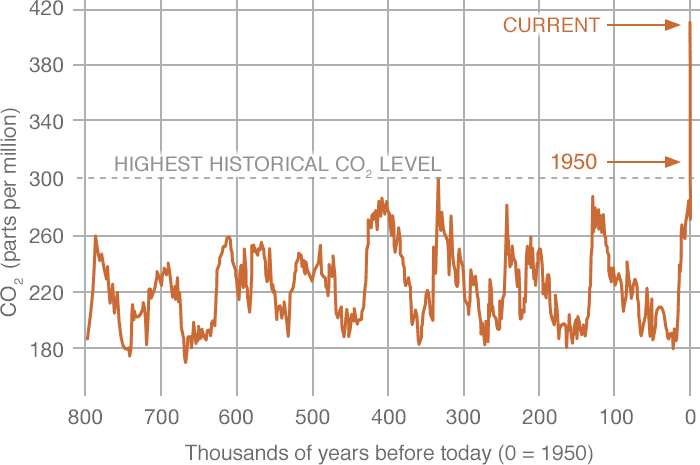



Carbon Dioxide Vital Signs Climate Change Vital Signs Of The Planet




Previewing The National Climate Assessment Climate Matters




Predictions Of Future Global Climate Ucar Center For Science Education



Temperatures Climate Action Tracker



Greenhouse
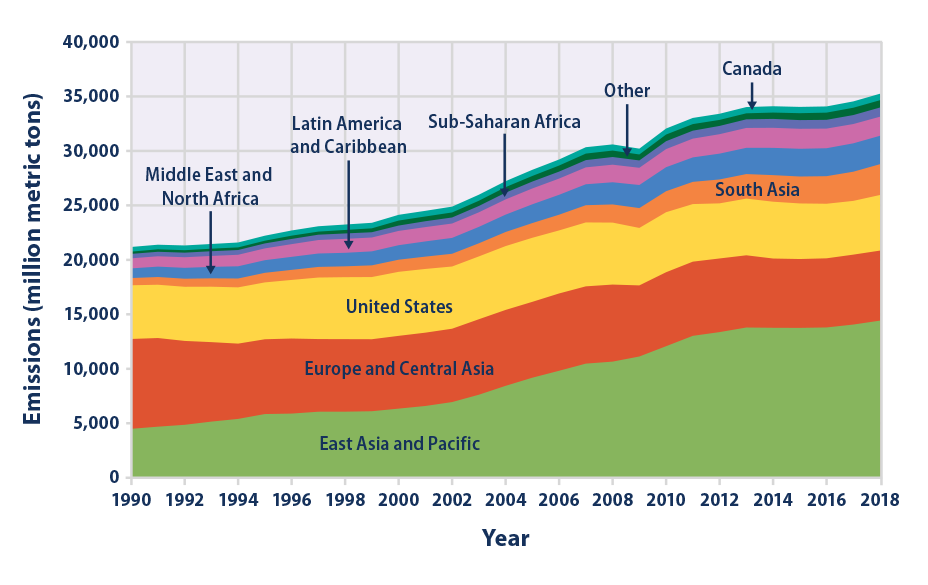



Climate Change Indicators Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Us Epa
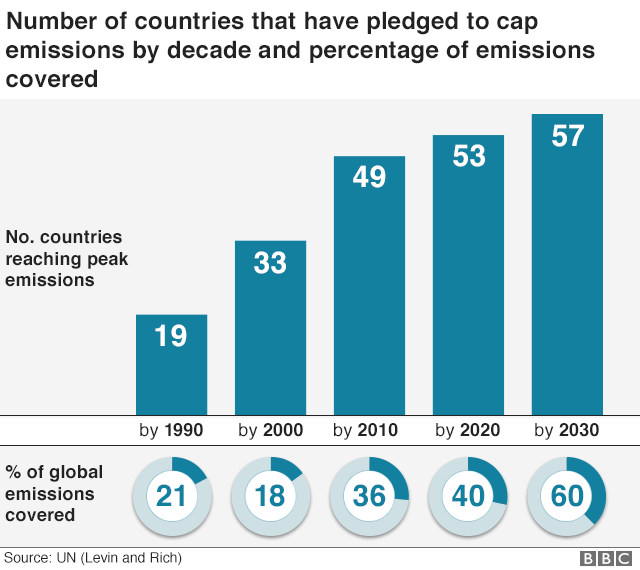



Climate Change Co2 Emissions Rising For First Time In Four Years c News




Global Warming Potential Effects Of Global Warming Britannica
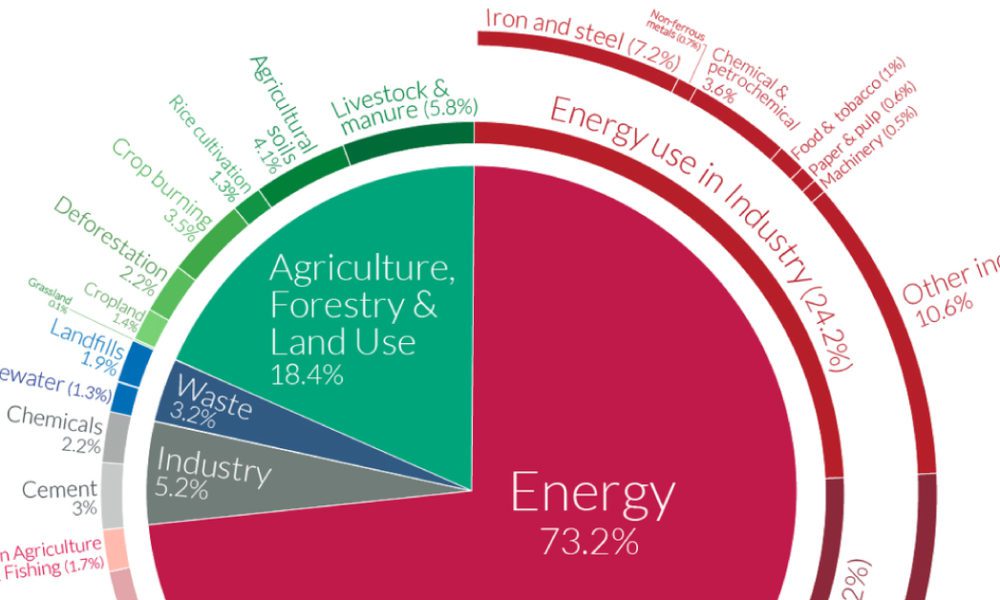



A Global Breakdown Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Sector
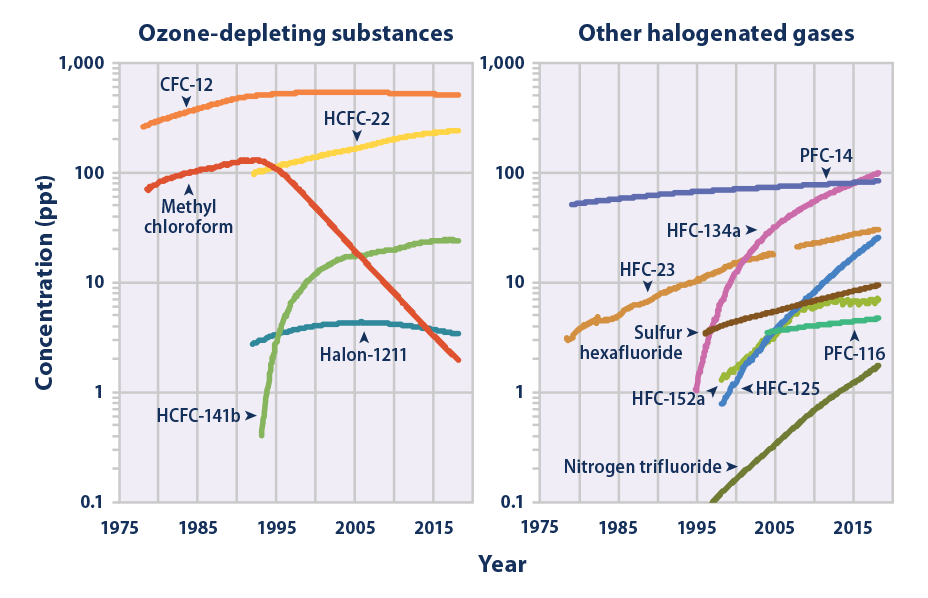



Climate Change Indicators Atmospheric Concentrations Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Major Causes Of Climate Change Globalecoguy Org




Climate Change And Agriculture Niwa




Global Warming Key Driver Of 15 S Record Heat Climate Central



Chart How Ambitious Is The Uk S Emissions Target Statista




Global Warming




Greenhouse Atmosphere Let S Heat Things Up Lesson Teachengineering
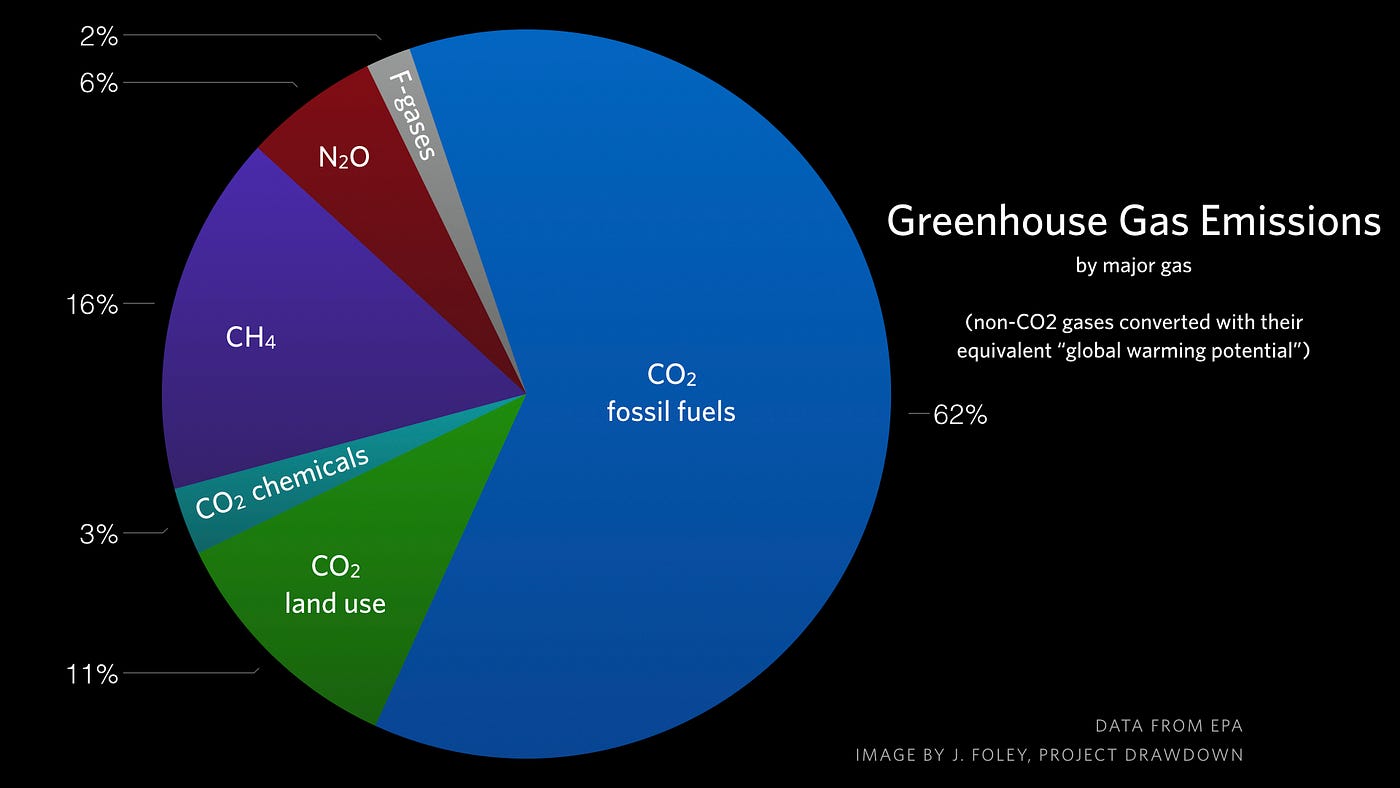



Major Causes Of Climate Change Globalecoguy Org




Greenhouse Gases Are Rapidly Changing The Atmosphere Climate Central



Climate Change International Ccs Knowledge Centre



Greenhouse Gas Global Greenhouse Warming



Greenhouse Gases And Temperature
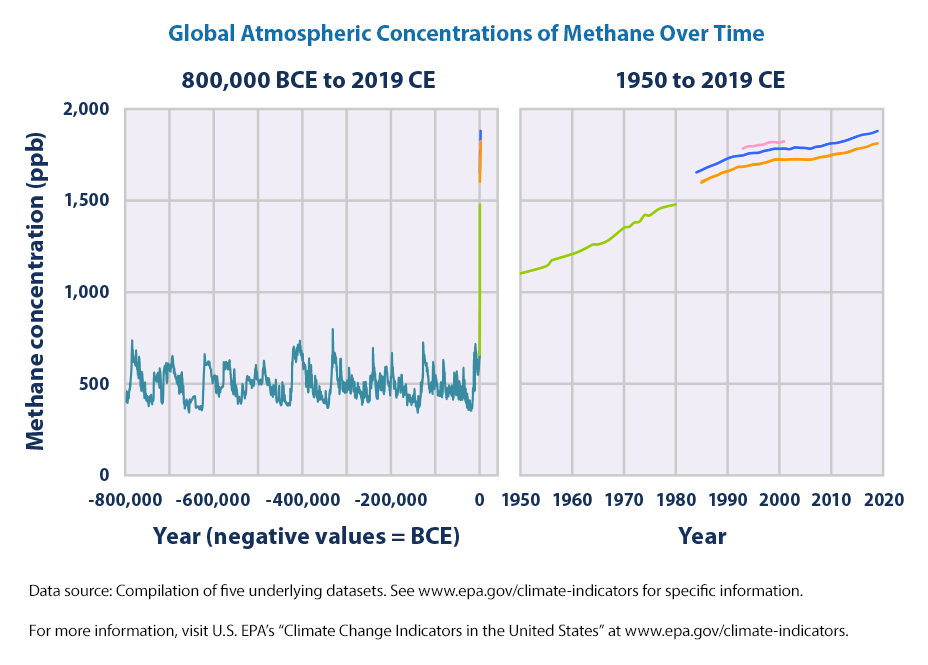



Climate Change Indicators Atmospheric Concentrations Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Each Country S Share Of Co2 Emissions Union Of Concerned Scientists
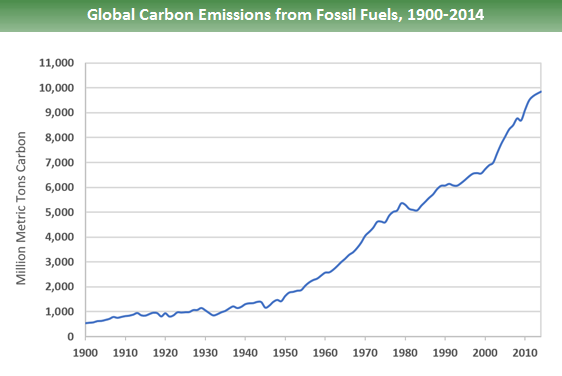



Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Data Us Epa



1




Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Country And Sector Infographic News European Parliament
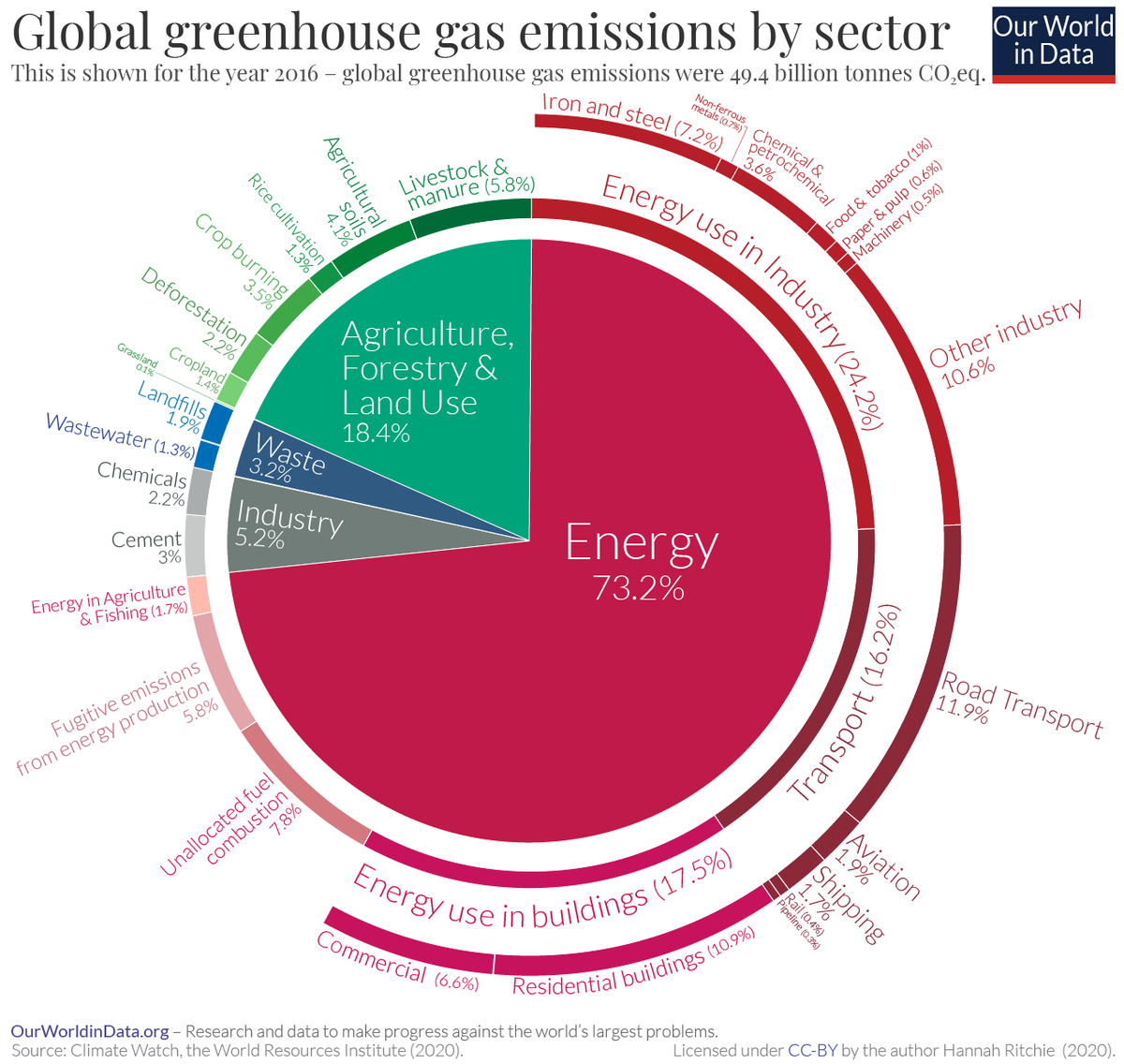



A Global Breakdown Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Sector




What S Really Warming The World Climate Deniers Blame Natural Factors Nasa Data Proves Otherwise



Co And Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data
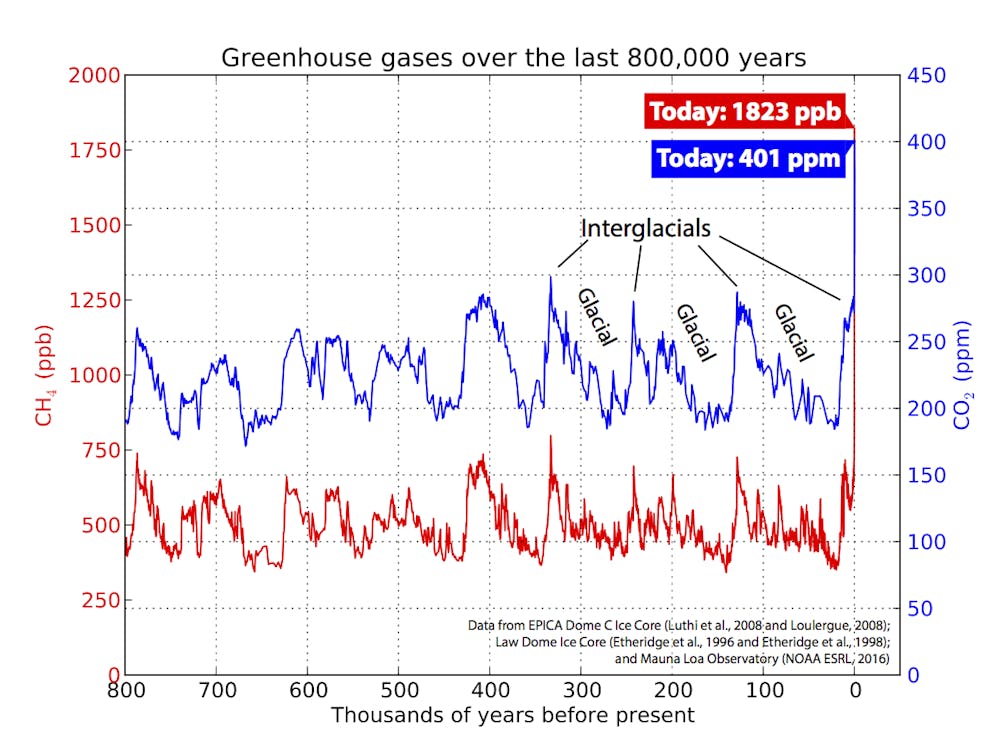



Mass Extinctions And Climate Change Why The Speed Of Rising Greenhouse Gases Matters
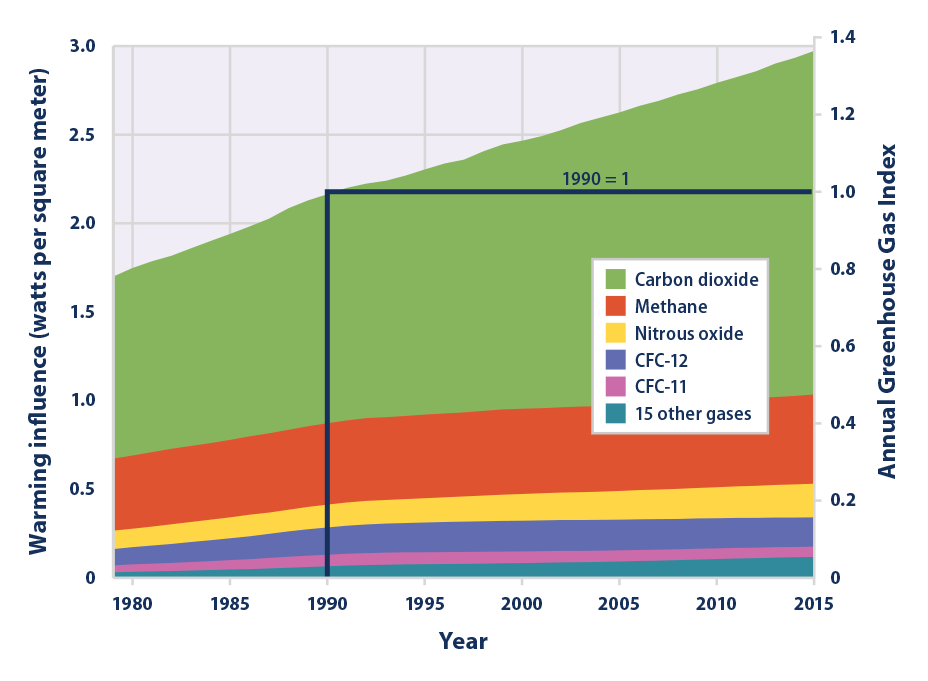



Climate Change Indicators Climate Forcing Climate Change Indicators In The United States Us Epa
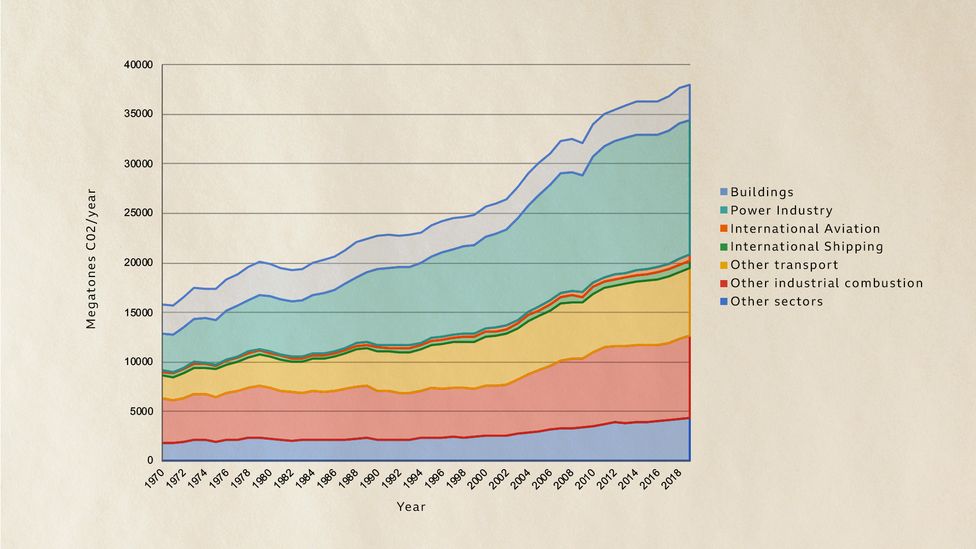



The State Of The Climate In 21 c Future
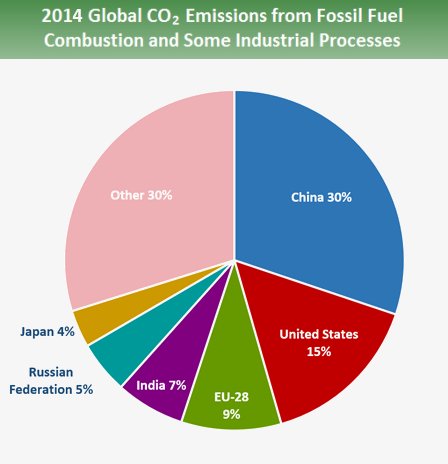



Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Data Us Epa
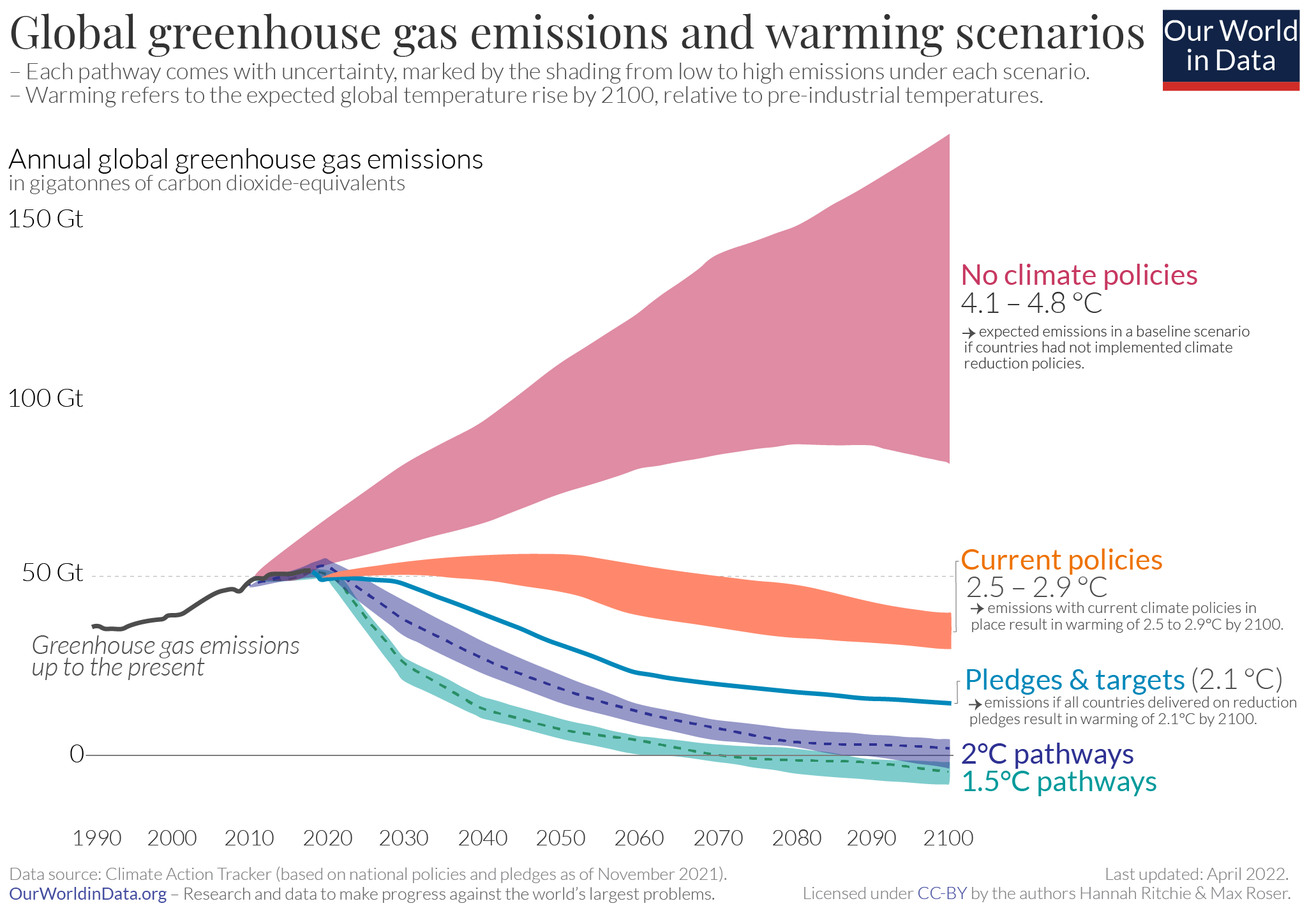



Future Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data
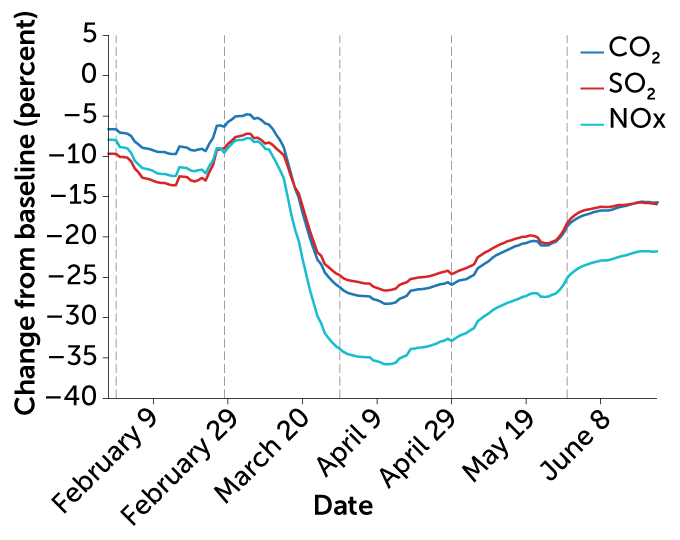



Covid 19 S Emissions Reductions Won T Impact Climate Change Science News




Cows Methane And Climate Change Let S Talk Science
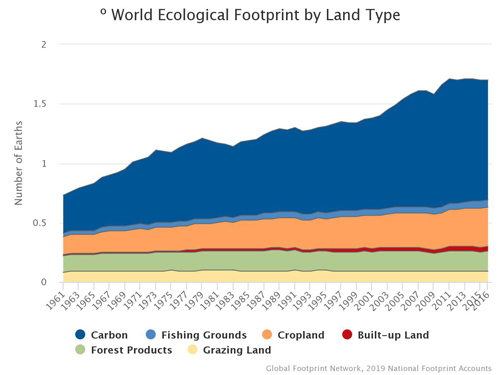



Climate Change The Carbon Footprint Global Footprint Network




Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Data Us Epa




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data



Greenhouse Conservation Biodiversity Sustainability Environment Issues Automated Lobbying Database At Information For Action



1




Noaa S Greenhouse Gas Index Up 41 Percent Since 1990 Welcome To Noaa Research




What S Going On In This Graph Nov 19 The New York Times




Cause And Effect For Global Warming Time For Change




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia



Chart Beef It S What S Contributing To Climate Change Statista




The World Isn T Doing Enough To Slow Climate Change Climate Central




Combating Climate Change A Global Commitment Foreign Policy



Co And Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data
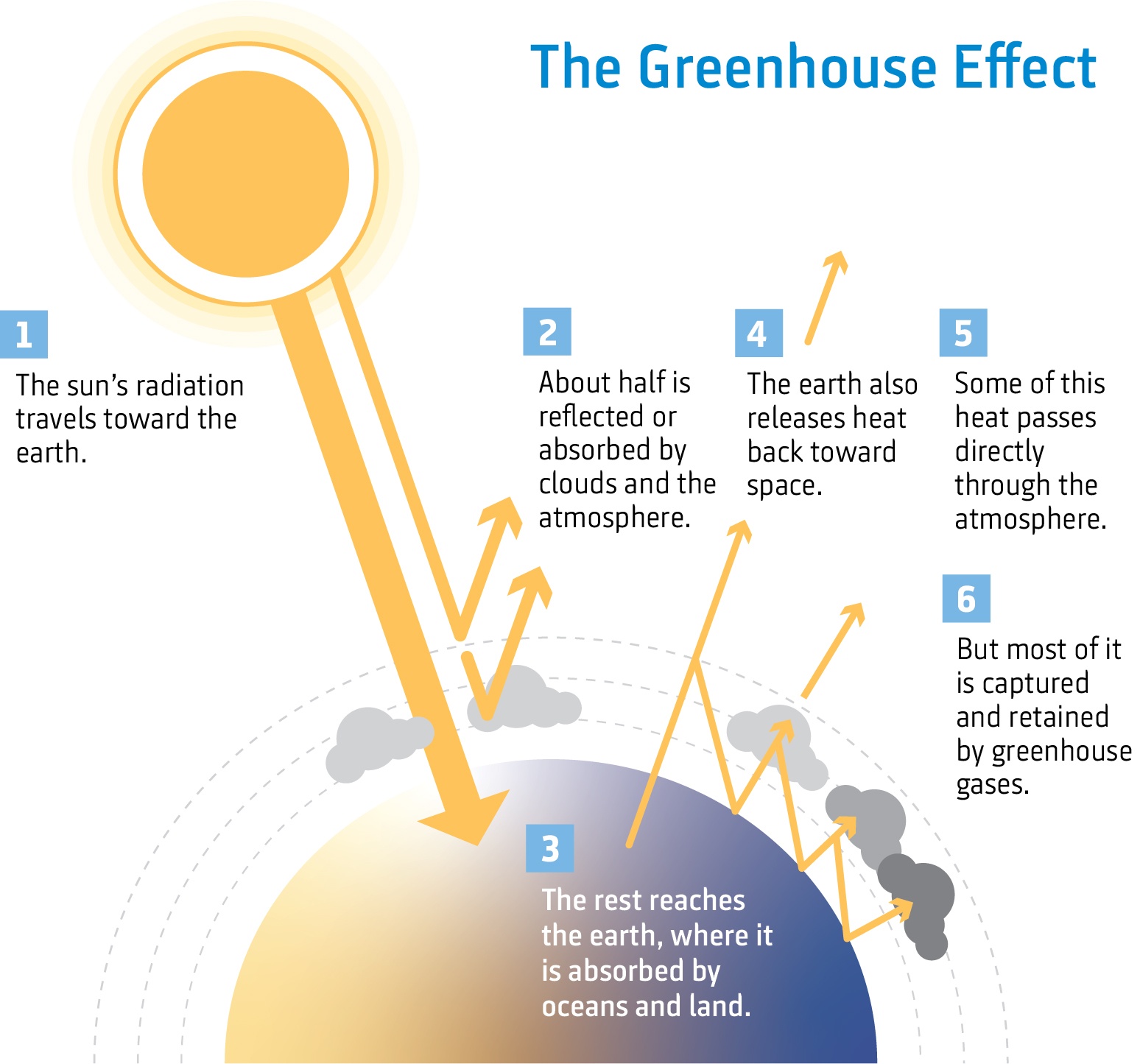



Climate Change The Science Niwa
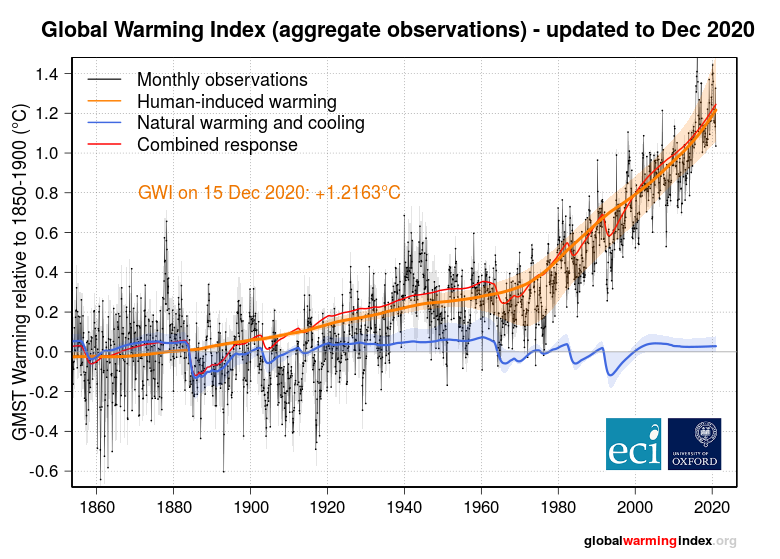



Globalwarmingindex Org Tracking Progress To A Safe Climate




Understanding The Science Of Climate Change
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/16185122/gw_graphic_pie_chart_co2_emissions_by_country_2015.png)



Climate Change Animation Shows Us Leading The World In Carbon Emissions Vox




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Plunged 17 Percent During Pandemic The Washington Post



Greenhouse Gas Emissions By The United States Wikipedia




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia
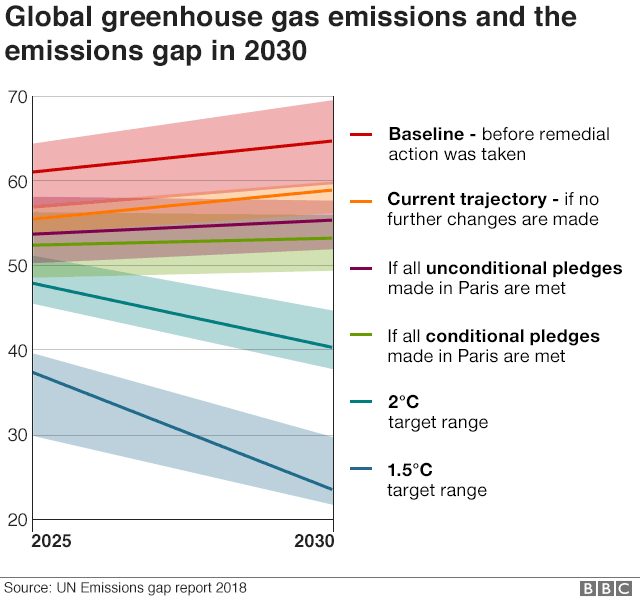



Climate Change Co2 Emissions Rising For First Time In Four Years c News




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa



Global Warming Research Issues
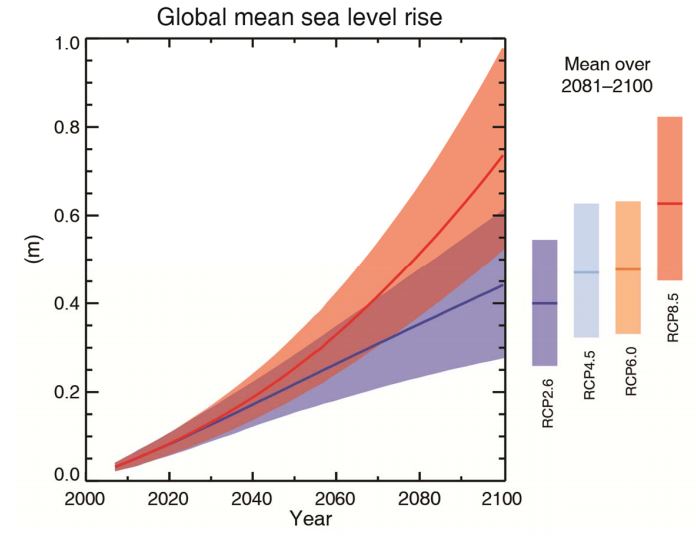



Ipcc Six Graphs That Explain How The Climate Is Changing Carbon Brief
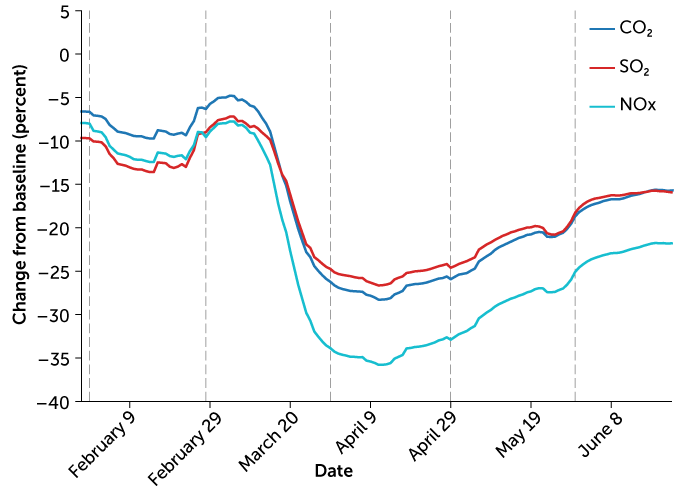



Covid 19 S Emissions Reductions Won T Impact Climate Change Science News



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿